Linear Solenoids Classification & Mechanism Applications Selection Factors Option Board
Selection Factors for Linear Motion Solenoid
Bear these factors in mind while selectiong linear motion solenoids, or fill out Application Condition & Requirement Form (Optiona Board)
A. Output Requirements
- Stroke / Force
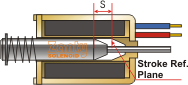
--Definition of Stroke: Displacement of plunger in reference to position of fully pulled in. (ref. bellow pictures)
--Solenoid generates force, which is changeable with stroke changes: bigger force at shorter stroke.
(Ideal Result: Solenoid’s stroke / force curve matching that demanded by application)
Pull Type Push Type 0 Stroke 

S Stroke 
- Response Time
Time from energizing solenoid to plunger achieving desired displacement. - Duty Cycle =On time /(On time+Off time)〕X100%
- Maximum on time
--Solenoid heats up while being energized. Duty cycle or maximum on time, and power of solenoid decide temperature rise of solenoid. --Temperature rise and ambient temperature decides selection of Insulation class.
(Insulation Class=℃: A=105, E=120, B=130, F=155, H=180, N=200, C=220+)
B. Input Conditions
- Power Supply Mode & Power
Input of different current wave shapes determines different motion mode of solenoid. Application may have: AC/DC (constant voltage / Current Supply, battery, dry cell, DC generator, capacitor), commutate and filer methods, voltage range and maximum current. - Diode as Rectifier:
If the power supply available for the solenoid is AC, a rectifier is required to convert it into DC. The rectifier should in principles be designed to be of full-wave rectificatino type. The rectifier elements should have a peak inverse voltage three times as high as the solenoid drive voltage. - Current (Power) is in proportion to force output within limited range. Force won’t increase any more with current (power) increase when solenoid gained magnetic saturation.
In the mean time: Temperature Rise increase in proportion to current (power)
C. Environment Factor & Life.
- Environment factors & expected life are critical for material and finish consideration.
- Environment factors include: temperature; humidity; magnetic or electric field; gas, liquid, dust pollutants or corrosives; impact or vibration, etc.
D: Connections of Assembling, Power Supply and Load; and Size:
- Assembly methods: a). external bolt. b). solenoid frame thread holes c). Fitting in
- Power supply connection method: a). Lead wire b). Lead wire + connector c). 187 quick connect terminals
- Load connection method:
.









E: Protection of Contacts in Driving Circuit.
| The control contacts for use with the DC Solenoid may spartk, wear and cause noise interference. Provide a proper protection as the case maybe. | |
| Resistor & Capacitor Method | Diode Insertion Method |
 |
 |